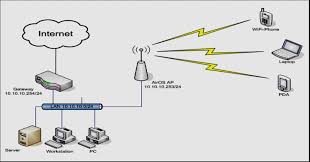
Wi-Fi Network:
Wi-Fi is a family of radio
technologies commonly used for wireless local area networking (WLAN) of devices.
It is based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. Devices that can use Wi-Fi
technologies include desktops and laptops, smart phones and tablets, smart TVs,
printers, digital audio players, digital cameras, cars and drones.
Compatible devices can connect to each other
over Wi-Fi through a wireless access point as well as to connected Ethernet
devices and may use it to access the Internet. Such an access point (or
hotspot) has a range of about 20 meters (66 feet) indoors and a greater range
outdoors.
Hotspot coverage can be as small as a single
room with walls that block radio waves, or as large as many square kilometers
achieved by using multiple overlapping access points.
Wi-Fi most commonly uses the 2.4 gigahertz
(12 cm) UHF and 5 gigahertz (6 cm) SHF ISM radio bands; these bands
are subdivided into multiple channels. Each channel can be time-shared by
multiple networks.
These wavelengths work best for
line-of-sight. Many common materials absorb or reflect them, which further
restricts range, but can tend to help minimize interference between different
networks in crowded environments.
Wi-Fi is potentially more vulnerable to
attack than wired networks because anyone within range of a network with a
wireless network interface controller can attempt access. Wi-Fi Protected
Access (WPA) is a family of technologies created to protect information moving
across Wi-Fi networks and includes solutions for personal and enterprise
networks.
To connect to a Wi-Fi LAN, a computer must be
equipped with a wireless network interface controller. The combination of
computer and interface controllers is called a station.
A service set is the set of all the devices
associated with a particular Wi-Fi network. The service set can be local,
independent, extended or mesh.
Each service set has an associated
identifier, the 32-byte Service Set Identifier (SSID), which identifies the
particular network. The SSID is configured within the devices that are
considered part of the network, and it is transmitted in the packets. Receivers
ignore wireless packets from networks with a different SSID.
Wi-Fi nodes operating in ad-hoc mode
refers to devices talking directly to each other without the need to first talk
to an access point (also known as base station).
There
are many different versions of Wi-Fi: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n (Wi-Fi
4), 802.11h, 802.11i, 802.11-2007, 802.11-2012, 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5),
802.11adj, 802.11af, 802.11-2016, 802.11ah, 802.11ai, 802.11aj, 802.11aq,
802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), 802.11ay.
|
Generation |
IEEE Standard |
Maximum Link rate |
|
Wi‑Fi 6 |
802.11ax |
600–9608 Mbit/s |
|
Wi‑Fi 5 |
802.11ac |
433–6933 Mbit/s |
|
Wi‑Fi 4 |
802.11n |
72–600 Mbit/s |
Equipment
frequently supports multiple versions of Wi-Fi. To communicate, devices must
use a common Wi-Fi version.
Uses:
Wi-Fi technology may be
used to provide Internet access to devices that are within the range of a
wireless network that is connected to the Internet.
Wi-Fi provides service in
private homes, businesses, as well as in public spaces at Wi-Fi hotspots set up
either free-of-charge or commercially, often using a captive portal webpage for
access. Organizations and businesses, such as airports, hotels, and restaurants,
often provide free-use hotspots to attract customers.
Routers that incorporate a
digital subscriber line modem or a cable modem and a Wi-Fi access point, often
set up in homes and other buildings, provide Internet access and
internetworking to all devices connected to them, wirelessly or via cable.
Similarly, battery-powered
routers may include a cellular Internet radio modem and Wi-Fi access point.
When subscribed to a cellular data carrier, they allow nearby Wi-Fi stations to
access the Internet over 2G, 3G, or 4G networks using the tethering technique. Some
laptops that have a cellular modem card can also act as mobile Internet Wi-Fi
access points.
Wi-Fi also connects places
that normally don't have network access, such as kitchens and garden sheds. A
number of other "wireless" technologies provide alternatives to Wi-Fi
in some cases:
- Bluetooth, short distance
network.
- Bluetooth Low Energy, a
low-power variant.
- Zigbee, low-power, low data
rate, and close proximity.
- Cellular networks, as used by
smartphones.
- WiMax, provide wireless
internet connection from outside individual homes.