Memory Management Concepts:
In a mono programming or uni-programming system, the main
memory is divided into two parts, one part for OS and another for a job that is
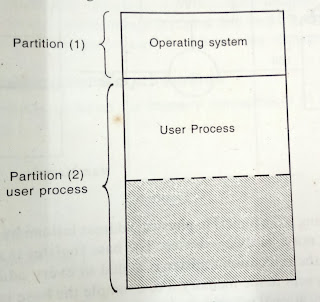
currently executing. Consider the following figure:
Fig: Main Memory Partition
Partition 2 is allowed for user processes. But, some part of
the partition 2 is wasted. It is indicated by Black lines in figure. In multiprogramming
environment, the user space is divided into number of partitions. Each
partition is for one process. The task of subdivision is carried out
dynamically by the operating system. This task is known as “Memory Management”. The efficient memory management is possible
with multiprogramming. As few processes are in main memory, the remaining
processes are waiting for an IO and the processor will be idle. So, memory
needs to be allocated efficiently to pack as many processes into the memory as
possible.
Logical vs. Physical Address Space:
An address generated by
CPU is called a logical address.
Whereas, an address generated by Memory
Management Unit (MMU) is called physical
address. For ex: J1 is a program
written by a user. The size of program is 100 KB. But, program is loaded in the
main memory from 2100 to 2200 KB. This actual loaded address in main memory is
called the physical address. The set of all logical addresses generated by a
program referred to as a Logical Address
Space. The set of physical address corresponding these logical addresses
referred to as a Physical Address Space.
In our ex: from 0 to 100 KB is the logical address space and 2100 to 2200 KB is
the physical address space.
Physical
address space = Logical address space + Contents of Relocation Register
2200 = 100 + 2100
Consider the
following fig:
The runtime mapping from logical to physical address is done by the Memory Management Unit (MMU), which is not a hardware device. The base register is also called the Relocation Register. The value in the relocation register is added to every address generated by a user process at the time it is sent to the memory. For ex: the base is at 2100, then an attempt by the user to access location 0 is dynamically related at location 2100. An access to location 100 is mapped to location 2200.

No comments:
Post a Comment