Assembler:
o
A computer can directly execute
only machine language programs that use numbers for representing instructions
and storage locations.
o
Hence an assembly language
program must be converted or translated into its equivalent machine language
program before it can be executed on the computer.
o
This translation is done with
the help of a translator program called assembler.
o
Assembler is system software
supplied by computer manufacturers.
o
It translates an assembly
language program into its equivalent machine language program.
o
It is so called because in
addition to translating it also assembles the machine language program in main
memory of the computer and makes it ready for execution.
o
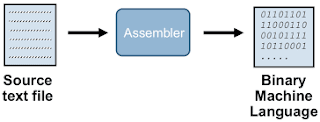
As the figure shows the input
to the assembler is assembly language program often referred as a source
program and its output is the machine language program often referred as object
program.
o
The assembler translates each
assembly language instruction into an equivalent machine language instruction. There
is a one to one correspondence between the assembly language instructions of a
source program and the machine language instructions of its equivalent object
program.
o
During the process of
translation of a source program into its equivalent object program by the
assembler the source program is not under execution. It is only converted into
a form that can be executed by the computer.
Compiler:
o
A computer can execute only
machine language programs directly.
o
Hence a high level language
program must be converted on translated into its equivalent machine language
program before it can be executed on a computer.
o
This translation is done with
the help of a translator program called compiler.
o
Hence a compiler is a
translator program that translates a high-level language program into its
equivalent machine language program.
o
As the figure shows input to
the compiler is the high level language program often referred as a source
program and its output is the machine language program referred as object
program.
o
Since high level language
instructions are micro instructions, the compiler translates each high level
language instruction into a set of machine language instructions rather than a
single machine language instruction.
o
Hence there is a one-to-many
correspondence between high level language instructions of a source program and
machine language instructions of its equivalent object program.
o
A compiler can translate only
those source programs that have been returned in the language for which the
compiler is meant.
o
Compilers are large programs
residing permanently on secondary storage.
o
To translate a source program,
the compiler and the source program are loaded first from secondary storage
into main memory of the computer.
o
The compiler being a program is
then executed with the source program as its input data.
o
It generates the equivalent
object program as its output is saved in a file on secondary storage.
o
To execute the program the
object program is loaded from secondary storage into main memory and executed.
o
In addition to translate in
high level language instructions into machine language instructions, compilers
also detect and indicate certain type of errors in source programs
automatically. These errors are referred as syntax errors and are of following
types:
1.
Illegal characters
2.
Illegal combination of characters
3.
Improper sequencing of instructions
4.
Use of undefined variable names
o
A compiler however cannot
detect logic errors. It can detect grammatical or syntax errors only in the
source program.
Interpreter:
o
Interpreter is another type of
translator used to translate high level language program into its equivalent
machine language program.
o
It takes one statement of the
high level language program, translate it into machine language instructions
and then execute the resulting machine language instructions immediately.
o
This is different from a
compiler that really translates the entire source program into an object
program and its not involved in its execution.
o
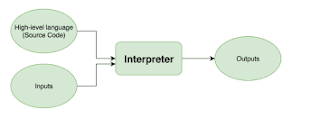
The input to an interpreter is
a source program button like a compiler its output is the result of program
execution instead of an object program.
o
After compilation of a source
program, the result in object program is a saved permanently for future use and
is used every time the program is to be executed. Hence repeated compilation is
not necessary for repeated execution of a program. However in case of an
interpreter since no object program is saved for future use repeated
interpretation of a program is necessary for its repeated execution.
o
As compared to compilers,
interpreters are easier to write because they are less complex programs than
compilers. They also require less memory space for execution than compiler
require.
o
The main advantage of
interpreter over compiler is that syntax error in a program statement is
detected and brought to the attention of the programmer as soon as the program
statement is interpreted. This allows the programmer to make corrections during
interactive program development. Therefore and operators make it easier and
faster to correct programs.
o
The main disadvantage of
interpreters over compilers is that they are slower than compiler when running
a finished program. This is because each
statement is translated every time it is executed from the source program. In case of compiler, each statement is
translated only once and saved in the object program. The saved object program
can be executed many times whenever needed and no translation of any statement
is required during the execution of the program. As the interpreter does not
produce an object program it must perform the translation process each time a
program is executed.
o
Assemblers, compilers and
interpreters are also referred as a language processors since they are used for
processing language instructions.

No comments:
Post a Comment