Terminal Network (Telnet):
·
The
main task of the internet is to provide services to users. For example, users
want to run different application programs at the remote site and transfer a
result to the local site. This requires a client-server program such as FTP,
SMTP. But this would not allow us to create a specific program for each demand.
·
The
better solution is to provide a general client-server program that lets the
user access any application program on a remote computer. Therefore, a program
that allows a user to log on to a remote computer. A popular client-server program
Telnet is used to meet such demands. Telnet is an abbreviation for Terminal Network.
·
Telnet
provides a connection to the remote computer in such a way that a local
terminal appears to be at the remote side.
·
There are two types of login:
Local Login
·
When a user logs
into a local computer, then it is known as local login.
·
When the
workstation running terminal emulator, the keystrokes entered by the user are
accepted by the terminal driver. The terminal driver then passes these
characters to the operating system which in turn, invokes the desired
application program.
·
However, the
operating system has special meaning to special characters. For example, in
UNIX some combination of characters has special meanings such as control
character with "Z" (^Z) means suspend. Such situations do not create
any problem as the terminal driver knows the meaning of such characters. But,
it can cause the problems in remote login.
Remote login
·
When
the user wants to access an application program on a remote computer, then the
user must perform remote login.
How remote login occurs?
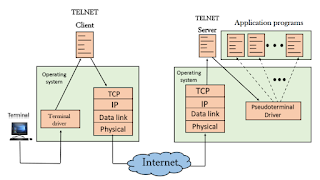
At the local site:
The user sends the
keystrokes to the terminal driver, the characters are then sent to the TELNET
client. The TELNET client which in turn, transforms the characters to a
universal character set known as network virtual terminal characters and
delivers them to the local TCP/IP stack.
At the remote site:
The commands in NVT forms
are transmitted to the TCP/IP at the remote machine. Here, the characters are
delivered to the operating system and then pass to the TELNET server. The
TELNET server transforms the characters which can be understandable by a remote
computer. However, the characters cannot be directly passed to the operating
system as a remote operating system does not receive the characters from the
TELNET server. Therefore, it requires some piece of software that can accept
the characters from the TELNET server. The operating system then passes these
characters to the appropriate application program.
Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
·
The
network virtual terminal is an interface that defines how data and commands are
sent across the network.
·
In
today's world, systems are heterogeneous. For example, the operating system
accepts a special combination of characters such as end-of-file token running a
DOS operating system ctrl+z while
the token running a UNIX operating system is ctrl+d.
·
TELNET
solves this issue by defining a universal interface known as network virtual
interface.
·
The
TELNET client translates the characters that come from the local terminal into
NVT form and then delivers them to the network. The Telnet server then
translates the data from NVT form into a form which can be understandable by a
remote computer.


No comments:
Post a Comment