TCP/IP Reference Model:
TCP/IP Reference Model is a four-layered suite of
communication protocols. It was developed by the DoD (Department of Defence) in
the 1960s. It is named after the two main protocols that are used in the model,
namely, TCP and IP. TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and IP stands
for Internet Protocol.
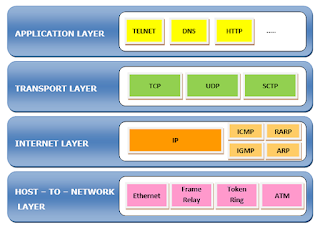
The four layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite are −
- Host-to-
Network Layer −It
is the lowest layer that is concerned with the physical transmission of
data. TCP/IP does not specifically define any protocol here but supports
all the standard protocols.
- Internet
Layer −It
defines the protocols for logical transmission of data over the network.
The main protocol in this layer is Internet Protocol (IP) and it is
supported by the protocols Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Internet
Group Management Protocol (IGMP), Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP),
and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
- Transport
Layer − It
is responsible for error-free end-to-end delivery of data. The protocols
defined here are Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram
Protocol (UDP).
- Application
Layer − This
is the topmost layer and defines the interface of host programs with the
transport layer services. This layer includes all high-level protocols
like Telnet, DNS, HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.
The following diagram shows the layers and the
protocols in each of the layers –
No comments:
Post a Comment