Priority Scheduling:
CPU is allocated to the highest priority of the process from the ready queue. Each process has a special number associated with called as priority number. If two or more processes have the same priority, then FCFS algorithm is applied for solving the tie.
The values of priority are not fixed. In some systems, lower
value denotes a lower priority, whereas in some systems lower value denotes
higher priorities. In our example, we are considering low numbers have the
higher priority.
Priority scheduling can be preemptive or non-preemptive. Priority
of the process can be defined either internally or externally. Internal priority considers the time
limits, number of open files, use of memory and use of IO devices. External priorities are set by using external parameter of the process like
importance of a process, cost of process, etc.
When the process arrives at the ready queue, its priority is
compared with the priority of the currently running process. A non preemptive
priority algorithm will simply put the new process at the head of the ready
queue.
A preemptive priority scheduling algorithm will preempt the
CPU if priority of the newly arrived process is higher than the priority of the
currently running process. In this, current executing process will change the
state from running to ready. In non preemptive scheduling algorithm, currently
executing process will not change state.
Consider the following set of processes with the burst time
in milliseconds. Arrival time of the process is 0.
|
Process |
Burst time |
Priority |
|
P1 |
3 |
2 |
|
P2 |
6 |
4 |
|
P3 |
4 |
1 |
|
P4 |
2 |
3 |
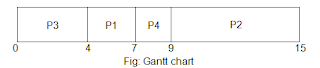
Processes arrive in the order P1, P2, P3, and P4. Gantt
chart, waiting time and turnaround time for priority scheduling algorithm are
as follows:
Waiting time:
|
Process |
Waiting time |
|
P1 |
4 |
|
P2 |
9 |
|
P3 |
0 |
|
P4 |
7 |
Turnaround time:
It is the sum of burst time + waiting time of
each process.
|
Process |
Turnaround time |
|
P1 |
3 + 4 = 7 |
|
P2 |
6 + 9 = 15 |
|
P3 |
4 + 0 = 4 |
|
P4 |
2 + 7 = 9 |
Priority scheduling algorithm can leave some low-priority
processes waiting indefinitely for the CPU. This problem is called starvation. Priority scheduling
algorithm faces the starvation problem. Starvation problem is solved by using aging technique. In aging technique,
priority of the processes will increase which are waiting for a longer time in
the ready queue.

No comments:
Post a Comment