Data Models in DBMS:
A data model is a collection of conceptual tools for
describing data - its relationships, semantics and consistency constraints. Data
models can be distinguished from one another on the basis of the relationship
among data, that is defined and the way the data is conceptually defined.
A primary objective that a data model serves is to evolve a
high level data model. It should assist the designer to incorporate a major
portion of semantics of database in the schema.
In DBMS, the data
models are broadly classified as:
1.
Object
based data models
2.
Record
based data models and;
3.
Physical
data models
1. Object Based Data Models:
These models are used in describing data at a logical and
view level. They have properties like they provide flexible structure in the
capabilities and allow us to specify data constraints explicitly. This model highlights
that everything is object having set of attributes.
Examples of data models that fall in this category are:
a)
Entity
relationship model
b)
Object
oriented model
2. Record Based Data Models:
The record based data models are used to describe data at a
logical and view level. However, they revolve around the records of database
and specify the overall structure of database with the help of value of
records. This is a key distinguishing factor between the record based and
object based model.
These models have got their name record based models because
the database is structured in fixed format records of several types. Each
record type defines a fixed number of fields or attributes and each field is
usually of a fixed length. This results in simple physical level
implementations of the database.
Examples of data models that fall in this category are:
a)
Relational
model
b)
Network
model
c)
Hierarchical
model
3. Physical Data Models:
This model is used to describe data at the lowest level. It
actually describes the behaviour of data at disk level. Furthermore, it also
describes the way data and data relationships that are maintained while storing
them on the disk. As such this leads to the way a DBMS is going to use
secondary storage devices for storing and accessing data.
Examples of data models that fall in this category are:
a)
Unifying
model
b)
Frame
memory model
A. Network Model:
The data in network model are represented by collection of
records. The relationships among data are represented by links, which can be
viewed as pointers.
Simply speaking, a pointer is a physical address which
identifies where the next record can be found on the disk or we can say that it
points to the next address location.
The network model allows each record to have multiple parent
and child records forming a lattice structure. Thus, network model supports many to many relationships. The
relationship between different records is called sets. This model is used as an easy way of representing objects and
their relationships. Following figure shows an example for network database:
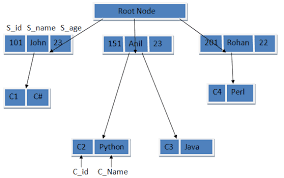
B. Hierarchical Model:
This model is very similar to network model, as in both the
models, the data and relationships among data are represented by using records
and links respectively. In this model, records are organized as collection of trees rather than arbitrary graphs.
The data storage is in the form of parent child relationship. An origin of the tree is called the root.
Data that follows the root is called a node and the last node in the series is called as a leaf node. Usually, there is one to many
relationship found in this model. Following figure shows an example for
hierarchical database:
Differences between Relational, Network and Hierarchical Models:
|
Parameter |
Relational model |
Network model |
Hierarchical model |
|
Relationship |
It supports one
to many and many to many relationships. |
It supports many
to many relationships. |
It supports one
to many relationships. |
|
Nature |
It is a table
based model, where a table is a collection of rows and columns. |
It is based on records
and links. |
It is based on tree
like structure having one root, several nodes and leaf nodes. |
|
Popularity |
This model is more
popular. |
This model is less
popular. |
This model is less
popular. |
|
Applications |
It has many applications, almost unlimited. |
It is an upgraded version of hierarchical model, so
used in the network. |
It is mainly used in mainframe and database system. |
|
Data relation |
This model uses
values to relate data. It does not use pointers or links. |
This model uses
links to relate data. |
This model uses
pointers to relate data. |
|
Storage |
The data is stored in the form of tables. |
The data is stored in the form of arbitrary graph. |
The data is stored in the form of a tree having parent - child
relationship. |

No comments:
Post a Comment