Attribute and its various types:
Attribute:
An entity is represented by a set of attributes. Attributes
are descriptive properties possessed
by each member of an entity set. Each entity has a value for each of its
attributes. For ex: a particular customer entity may have the value 12345 for Customer-ID.
For each attribute there is a set of permitted values called
the domain, or value set of that attribute. The domain of attribute customer name
might be the set of all text strings of a certain length.
Types of attributes:
1.
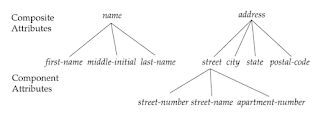
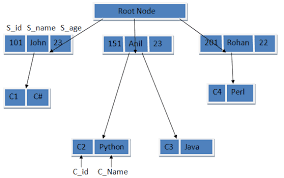
Simple and Composite Attribute:
If attributes cannot
be further divided into sub-parts then they are known as simple attribute. Composite attributes on the other hand can be divided into sub parts. For ex: an attribute name
would be structured as a composite attribute consisting of First-name, Middle-name,
and Last-name.
Fig: Example of composite attributes
2.
Single and Multi-valued attributes:
The Loan-number attribute for a specific loan entity refers
to only one loan number. Such attribute is called as single valued attribute. There may be instances where an attribute
has a set of values for a specific entity. Consider an employee entity set with
the attribute phone number. An employee may have zero, one or several phone numbers
and different employees may have different numbers of phones. This type of
attribute is said to be multi-valued
attribute.
3.
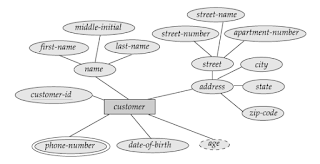
Derived attributes:
The value for this type of attribute can be derived from the values of other related attributes or
entities. As an example, suppose that the Customer entity set has an attribute age
which indicates the customer’s age. If the customer entity set also has an
attribute date-of-birth, we can calculate age from date of birth and the
current date. So, age is a derived
attribute. In this example, date-of-birth may be referred as a base attribute.
Fig: Example of composite,
multi-valued and derived attributes
4.
Null attribute:
An attribute takes a null value when an entity does not have a value for it. Null
value may indicate not applicable,
i.e. the value does not exist for
the entity. For ex: one may have no middle name. Null can also designate that
an attribute value is unknown. An
unknown value may be either missing or
not known.